During an effort, the acid-base balance of the horse’s body is disturbed. By using more oxygen and energy, his metabolism produces waste products that acidify his body. Then, the body naturally regulates its pH level in order to maintain this acid-base balance.
How does the horse’s acid-base balance work during exercise?
What are the consequences of a potential unbalance?
What can be done about it?
Acid-base balance – Definition
The horse’s body, like any organism, functions through different metabolisms. These are dependent on two regulating parameters: body temperature and pH level.
The average body temperature of a horse is between 37.5°c and 38°c. The pH or “Hydrogen Potential” determines the degree of acidity of a solution. The pH measurements describe the concentration of H+ ion molecules in a solution. A pH below 7 is said to be acidic, while a pH above 7 indicates that it is an alkaline solution. The pH in horses is between 7.0 and 7.4. The more acidic an aqueous solution is, the more H+ ions it will contain.
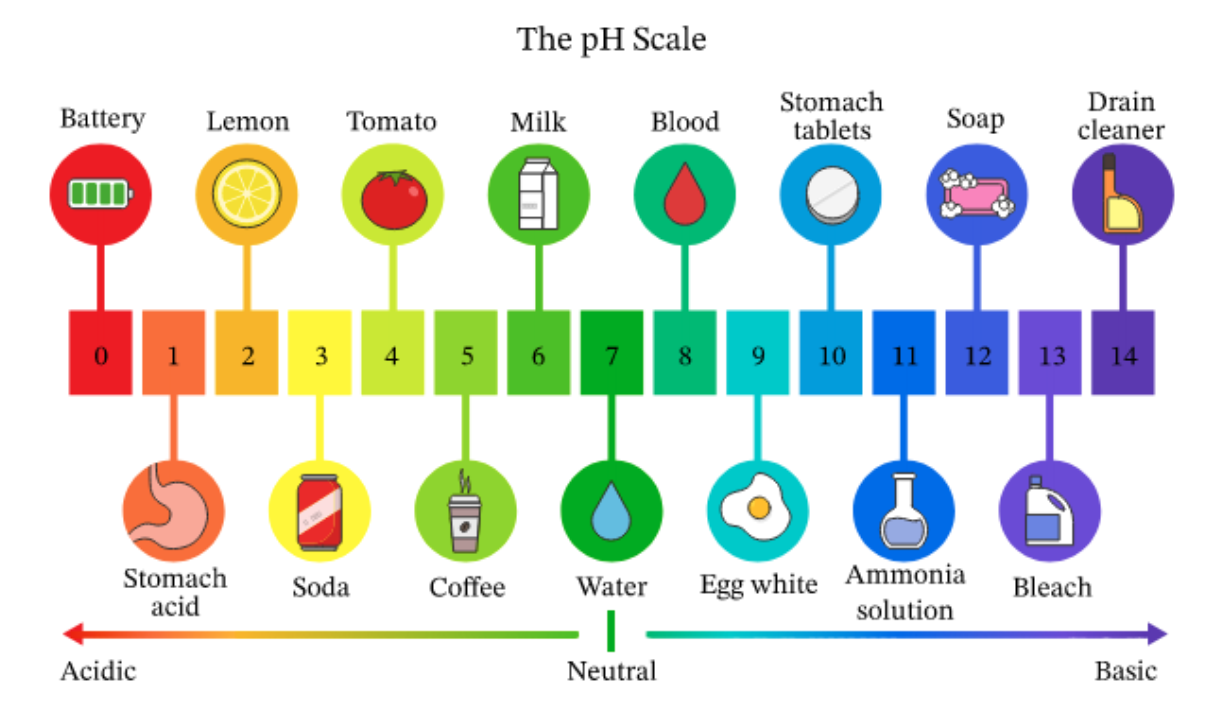
Source : www.nagwa.com
Cells continuously produce H+ ions, which is why the body naturally regulates them via the pH level in order to maintain a balance between the acidity and alkalinity ratio of his body. This is known as the acid-base balance.
There are two forms of acids regulated by the body:
- Volatile acids: these are the acids that are released by the lungs in the form of CO2.
- Fixed acids: these are acids that are eliminated by the body through the kidneys.
How does a horse’s acid-base balance work during exercise?
During an exercise session, the horse consumes more energy and oxygen than when he is at rest. In response to this effort, the body produces a lot of heat and waste products, which need to be eliminated. One of these waste is lactic acid, which is a residue produced by the muscle cells when they are starved of oxygen. It is lactic acid that is responsible for the muscle pain that occurs after intense effort.
➡️ To find out more about energy creation, we recommend you this article.
In anaerobic lactic conditions, glucose is used and converted into lactic acid, which is then split into lactate and H+ ions. This accumulation of hydrogen is stored in the muscles and acidifies the horse’s body. It is this unbalanced pH level that alters the contractibility of the horse’s muscles and contributes to muscle fatigue during high intensity exercise.
What are the risks of an over-acidic body?
We have seen that when the body makes an intense effort, its acid-base balance is disturbed. The muscles lose their contraction strength and their capacity to produce ATP.
This acidity contributes to fatigue during exercise, muscle aches, cramps and incomplete recovery. It favours the appearance of inflammatory phenomena and injuries such as tendonitis, because neither the kidneys nor the lungs are able to evacuate them completely.
Inflammation can occur because of high acidity in the body. The horse’s intestinal wall can become inflamed and less resistant to pathogens and toxins in the diet. This is known as gut acidosis. This can lead to a number of digestive and immune complications and increase the risk of ulcers.
Food, through digestion, is thus an aggravating factor in acid-base imbalance. Indeed, the horse, a herbivore by nature, is adapted to a slow and continuous ingestion of slow starch foods, such as grass or fibres. The fibre provided by the diet is no longer sufficient to meet the energy requirements of athletic horses, such as racehorses. Therefore, common feeding practice is to supplement the forage with energy-rich cereal-based concentrates. This excess starch is not digested in the small intestine and is fermented in the colon, which produces lactate that increases acidity levels in the gastrointestinal tract. This overly acidic diet causes the horse’s body to rebalance the pH level, producing salts. These calcium and magnesium salts then become lodged in the tendons, causing joint pain and tendonitis.

Source: phileo-lesaffre.com
Salivation plays an important role in maintaining an ideal pH, as it facilitates, among other things, digestion. For this reason, chewing throughout the day is recommended to promote the production of saliva.
How can a good acid-base balance be restored?
In order to restore a good acid-base balance that can be disturbed by exercise and diet, there are some solutions.
The first is through nutrition. Horses should have access to as much or as little forage as possible to keep their stomachs full. As previously mentioned, it is chewing, by producing saliva, that helps to reduce stomach acidity caused by feeding too much starch.
Bicarbonate can also be useful, among other things, in reducing the threshold for short-term fatigue, such as in a sprint. Thanks to its alkaline pH, bicarbonate helps to neutralise stomach acid. Many food supplements exist for this effect.
It is also recommended to ensure that the horse is properly hydrated, as a lack of water sensitises the tendons and leads to tendonitis. In this way, electrolytes can help to regulate the nerve and muscle function, and thus maintain the acid-base balance.
Conclusion
The acid-base balance of the horse is a real regulator and is necessary for the proper functioning of the horse’s body. A disturbance of his pH can have an impact on his health and his performance. It is therefore important to follow your horse’s behaviour in order to react quickly by re-establishing a good balance between the acidity and alkalinity of its body.
Sources:
Equilibre acido-Basique – aliments complémentaires pour chevaux Pommier Nutrition. Available at: https://www.pommier-nutrition.com/dossiers/equilibre-acido-basique (Accessed: 29 June 2023).
L’équilibre acido-Basique – paolo-diet-angelis.fr. Available at: https://www.paolo-diet-angelis.fr/post/l-%C3%A9quilibre-acido-basique-simple (Accessed: 29 June 2023).
Poulain, D., nutri, D. and Antoine Équilibre acido-basique : L’organisme Peut Gérer, Lepape. Available at: https://www.lepape-info.com/nutrition/equilibre-acido-basique-lorganisme-peut-gerer/ (Accessed: 29 June 2023).
Équilibre acido-basique et nutrition sportive (2022) IRBMS. Available at: https://www.irbms.com/equilibre-acido-basique/ (Accessed: 29 June 2023).



