Every winter, trainers welcome young horses to their stables. These horses have been broken in and pre-trained and are now ready to start their career. This first period of work is critical for the horse’s career, and numerous benefits may be acquired by collecting and analyzing data from the beginning of their training. The seven most important reasons to monitor your young horses are as follows.
1. Build a database from the beginning of training
Data is any information on a horse’s pedigree, performance, or health. The collection of this information requires a specific approach that can be summarized in three words: creation, enrichment, and updating.
It is commonly understood that raw data, without any context or element of comparison, adds little value. As a result, it’s a good idea to keep note of your yearlings’ first training sessions so you can begin creating their database from the start. Data collection will significantly enrich this first stage of production as they progress. Finally, a few months later, for example, before the first race, the data collection allows you to update the data that helped in the development of this database.
2. Detect a racehorse’s precocity
After having enriched the database with different young horses, it’s time to draw some comparisons. A horse with a high heart rate and exceptional speed will stand out among the other young horses who began at the same time. As a consequence, the data may be used to emphasize a horse’s precociousness and, as a result, to personalize his training so that it is tailored to his level and needs.
Three speed data are then useful: the maximum speed, the time to cover the best 200m and the best 600m. These three indicators can be compared with data measured during the race.
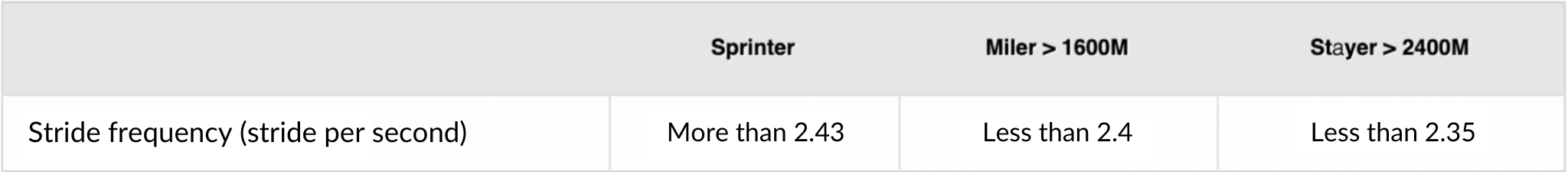
3. Identify the locomotor profile and determine the theoretical racing distance
Starting a racehorse’s training is a complex task that needs careful consideration of several elements. As a result, the data is a valuable solution for enhancing the trainer’s abilities. When selecting a race, the trainer needs obviously to consider the distance, and locomotion data can assist you in making the most objective decision possible. Many scientific research have been conducted to determine the appropriate distance based on the locomotor characteristics of a horse. The analysis is based on a study of the stride lenght and stride frequency of a horse’s locomotor profile. As each horse has its own stride style, generic and theoretical profiles may be identified, with a defined ideal distance.
4. Analyze fitness and assess the training’s impact
It is feasible to assess the impact of the training because if the database was built from the start. Indeed, the data evolution over time measures and quantifies the horse’s physiological transformation. Thoroughbreds are strong athletes that are well-known for their capacity to adapt physiologically and physically throughout training. Thus, training a juvenile racehorse is a delicate balancing act between developing its cardiac function and aerobic capacity and putting strain on the musculoskeletal system, which can possibly induce structural damage and/or lameness. Heart rate indicators are good indicators of a young horse’s potential. Monitoring and analysing the heart rate of a racehorse provides information on his fitness level and his adaptation to training. The data can be used to gradually increase the training load by dosing well between under- and overtraining.
24/04/21


23/06/21
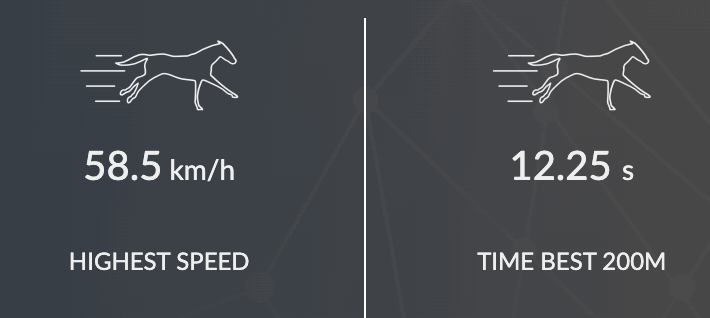
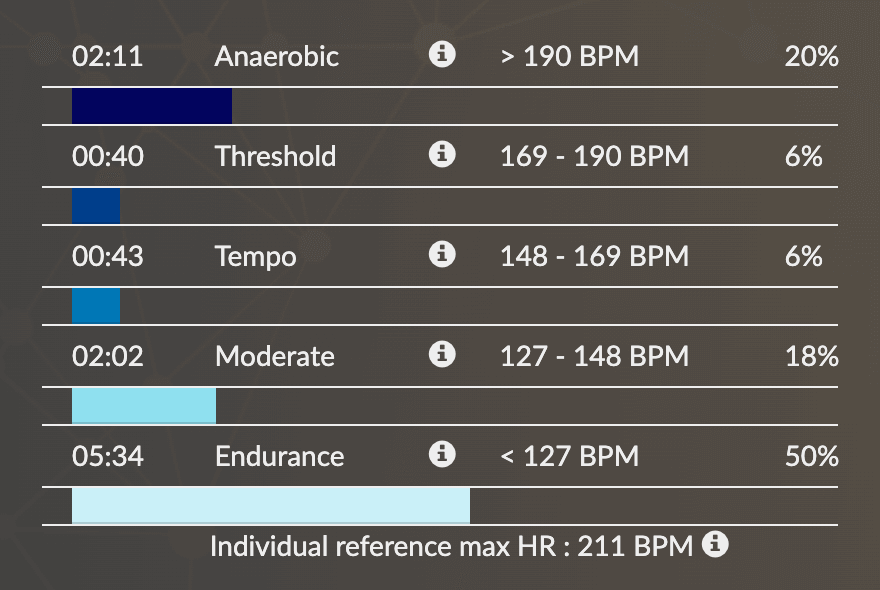
The data in the preceding example is from a 2-year-old horse who began training in early 2021. The trainer has been closely monitoring this young horse’s training sessions. We can trace this horse’s improvement thanks to this data: between April and June, he is able to run faster and in better cardiac condition. Despite the increased pace, the time spent in the anaerobic zone has decreased by 10 seconds. His body has adapted, demonstrating the training effectiveness.
Furthermore, stride data, such as stride length, stride frequency, regularity, and symmetry, are particularly useful in monitoring the development of muscle stiffness or lameness. With these indicators, you may analyze the influence of your training on your horses’ musculoskeletal system.
5. Ensure that your racehorses are ready to advance in their training
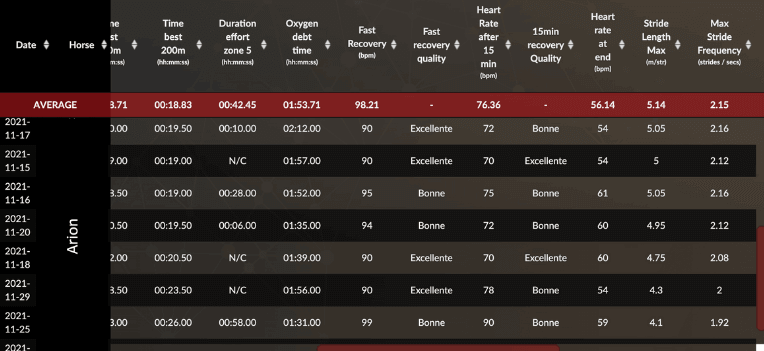
Before going on to the next stage of training, you may employ data to confirm your horse’s current fitness. It is critical to establish a routine and a safe place for young horses in order to preserve their health and morale. The information will assist you in determining if your yearlings have reached the necessary fitness level to manage increased effort. In tangible words, you may track the progression of recuperation. If it improves over time and stabilizes in the last few training sessions, it indicates a change to a higher level of fitness.
Let’s take a look at Arions’ data, a two-year-old horse. We can see that the horse did not recuperate well after the strenuous training session. Perhaps he wasn’t quite ready to raise the intensity of his training (from 53.7 km/h to 58 km/h). On the 8th of December, the horse did a session with the same intensity as on the 7th of August. The horse’s data showed a considerable increase in recovery between the two sessions. During November and December, the trainer presumably monitored the horse’s work to determine that he was ready to progress to the next level of training. We can tell from the data that this horse was ready for his session on the 15th when he peaked at 60km/h. His recovery is described as being very good.
6. Reduce the injury risk
As previously stated, exercise can trigger muscle remodelling, which can result in structural injury and/or lameness. Training has a significant impact on the cardiovascular system as well. It is vital to monitor the data gathered for irregularities in order to reduce the risk of injury or the development of respiratory disease. A rapid and inexplicable spike in HR might indicate discomfort, tension, or terror. HR spikes or abnormal HR during warm-up can be utilized to detect early indicators of pathology.
Arion’s heart rate is over 250 BPM from the start of the gallop. This abnormally fast heart rate is a health warning sign that might suggest a cardiac disease. This discovery is noteworthy for multiple training sessions of this horse. The ECG obtained automatically during the same training session might be analyzed after a consultation with a veterinarian. A heart arrhythmia was found. This heart issue must be explored since, if left untreated, it might lead to sudden death. Because the trainer has been monitoring the horse in a timely manner, he may contact his veterinarian to investigate and perhaps treat the arrhythmia.
7. Profile the data of a successful horse thanks to the longitudinal follow-up
If one of the two-year-olds you’ve been observing in training has a successful career, his data becomes a reference for a good racehorse’s data profile from a young age. By comparing this horse’s data to that of your young horses, you may quickly discover potential performers in your stable.
In order to carry out the longitudinal monitoring of a racehorse, the most effective way is to carry out a standardised exercise when the horse arrives at training, and then on a recurrent basis. This exercise clearly shows the horse’s progress and makes it possible to check whether the programmed training is appropriate and effective. The data, taken from the standardised exercises, are then comparable and relevant throughout the season.
This data then offers objective support for decision making and supports your feelings about the condition of your two-year-old. Followed throughout his career, a horse has a life book of his career, and this set of data can be used again as a reference when welcoming the next generations.
Keywords: young horses, race, data base, training, monitor, evaluate